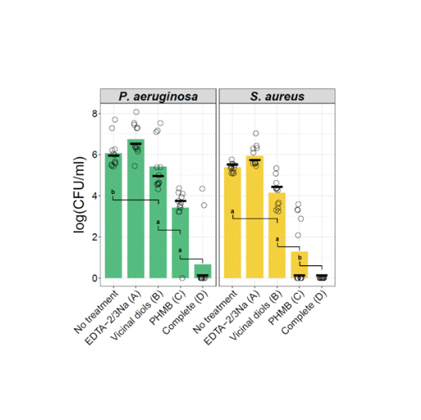
Synergy of the components was determined by Kull equation analysis based on MBEC peg biofilm assay results utilizing mono-species P. aeruginosa and S. aureus (MRSA) biofilms.
The complete BIAKŌS™ ANTIMICROBIAL SKIN AND WOUND CLEANSER reduced the viability of P. aeruginosa mono-species biofilms by more than 5 logs and eliminated Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).